 Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika viruses are transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes and are currently circulating in the Caribbean. Early symptoms of these illnesses include fever, headaches, and flu-like body ache.
Dengue, Chikungunya, and Zika viruses are transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes and are currently circulating in the Caribbean. Early symptoms of these illnesses include fever, headaches, and flu-like body ache.
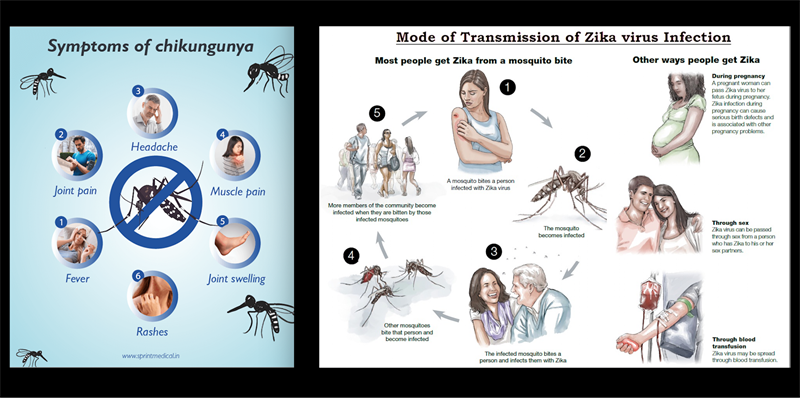
Chikungunya has an incubation period of 3–7 days and causes joint pain and morning stiffness, often accompanied by a maculopapular rash. Severe cases may lead to brain inflammation, heart and lung failure, kidney failure, or death, especially in older adults or those with chronic conditions.
Zika’s incubation period is 2–14 days and can cause fever, an itchy rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis. It is linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome and, in pregnant women, can cause congenital microcephaly and fetal loss.
Fact sheet on Chikungunya - PAHO
- The word comes from the African Makonde language and means "bent over in pain."
- The disease was first described in Tanzania in 1952 and the virus was first isolated in Thailand in 1958.
- Chikungunya is not transmitted from one person to another. The virus needs a vector as a means of transportation: mosquitoes (Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus).
- The evidence available at this time demonstrates that Chikungunya virus infection produces lifelong immunity. The disease can be acquired only once due to the presence of antibodies that protect against future infection by the virus.
- The disease is endemic in the Americas, except in Canada, Chile, the United States and Uruguay.
- The treatment is symptomatic and in 98% of outpatient cases. Bed rest should be kept, preferably using mosquito netting. For pain and fever, it is recommended to take Acetaminophen or Paracetamol, to control the fever. It is necessary to drink plenty of liquids (water, coconut water, soups, fruit juices, oral rehydration serum).
- There is currently no vaccine or specific drug against the virus.
- Cases of death from chikungunya are very rare and are almost always related to other existing health problems. Patients suffering from comorbidities or extreme health conditions in life have a greater risk of presenting serious forms and fatal outcomes due to this illness.
- Mothers who have chikungunya during pregnancy do not transmit the virus to their babies. However, there are documented cases of mother-to-child transmission when the mother has a fever in the days immediately before delivery or during delivery.
Key Facts About Zika - PAHO
- The virus was isolated for the first time in 1947 in the Zika forest in Uganda. Since then, it has remained mainly in Africa, with small and sporadic outbreaks in Asia.
- In 2007, a major epidemic was reported on the island of Yap (Micronesia), where nearly 75% of the population was infected.
- In May 2015, the public health authorities of Brazil confirmed transmission of the Zika Virus in the country's northeast. In July 2015, it was discovered that ZIKV was associated with Guillain-Barré syndrome. In October, it was also linked to central nervous system malformations at birth, which includes microcephaly.
- In February 2016, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared ZIKV-related microcephaly a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). However, in November 2016, WHO declared the end of the emergency.
- Zika now is endemic in the Americas.